
Welcome students,
We now discuss properties of fluids. Previously we had chapter as properties of Matter. Now we have three chapters defined as properties of solids, properties of liquids and thermal properties of matter. In first part is properties of solids in which we study of properties of solids. Terms are Young’s modulus, bulk modulus and modulus of rigidity . Here we discuss episode basically properties of fluids now these properties are also divided as when liquid or fluid is moving or at rest. Firstly will discuss when fluids are at rest hence also termed as hydrostatics .
HYDROSTATICS
Fluids is the definition for something which is flowing, that simply means liquid and gas .
First term is definition of pressure : what is force per unit area . Unit given as is Newton/metre². For any fluid the pressure at bottom depends on the height of liquid column, which is given as pressure equals to
P = hρg
P is pressure, h is height of liquid column and ‘ρ’ is density of liquid and ‘g’ acceleration due to gravity
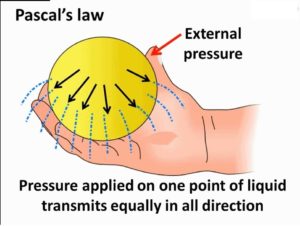
Then comes Pascal Law in which it is stated that for a confined liquid, pressure is equally transmitted in all directions, be careful it is not distributed but transmitted . Based on this law we use two devices Hydraulic lift and Hydraulic brake .
Then we discuss about atmospheric pressure, : atmosphere has got its own pressure due to height of atmosphere. Here the height of atmospheric pressure is roughly extended till 8 km. Atmospheric pressure was first measured by Torricelli and which comes out to be 760 mm of Mercury . Manometer is a device to measure pressure difference across U tube .
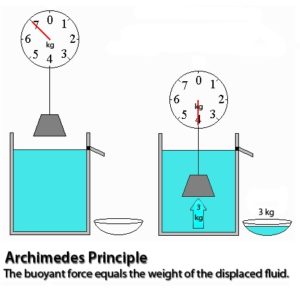
Archimedes principle states that whenever a body is partially or fully immersed in a fluid, it experiences an up thrust which is equal to weight of the liquid displaced. Thus effective weight is reduced. Effective weight is also termed as Apparent weight.
Surface of every liquid is under tension, and behaves like a stretched membrane. Surface tension is defined as force on imaginary line drawn on the surface of liquid. Hence has the unit of Newton/meter
Next we define surface energy. Surface energy is defined as energy required to create a unit surface . It is defined as work done per unit area and is numerically equal to surface tension. To find the complete energy we multiply surface tension area .
Surface energy = Surface Tension × Area
Every drop or bubble is spherical because the sphere has the least energy for a given volume. Now less area means less surface energy and hence the shape. You can see it for small drops when the weight is not much and its effect can be neglected. Thus every bubble or drop has excess pressure in it. This excess pressure depends on surface tension and radius of drop. Please do remember that bubble has two surfaces and a drop has only one surface.
Angle of contact is defined as the angle between the tangent to solid and liquid surfaces at a point of contact inside the liquid.” It depends upon the nature of solid and liquid. For concave meniscus it is acute while for convex it is obtuse. Basically it depends on the nature of forces between solid and liquid, and liquid and liquid. Hence depends on the cohesive and adhesive forces. Force between liquid and solid constitute the adhesive force and force between liquid molecule and same liquid molecules is cohesive force. Angle of contact is acute when adhesive force is greater than cohesive force, and when adhesive is less than cohesive force angle of contact is obtuse. Angle is acute when water is in glass and obtuse when mercury is in glass as a special case alcohol kept in steel glass is zero degree.
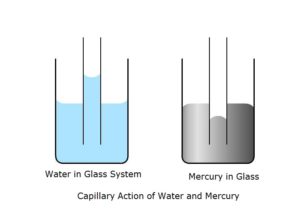
Capillary tube :A tube with very fine bore or hole is called a capillary tube. When the hole is very small the inside surface becomes part of a sphere. Excess pressure of the drop can be utilised here. When drop is inside air is outside we have excess pressure, but when air is inside and liquid is outside we have reduction in pressure due to this liquid rises in capillary. Formula is also given for that. When two bubbles coalesce to form a large interface or when two drops combine to form a single drop the new radius formula is also given here.
Now a very important concept is used, when ‘n’ number of liquid drops coalesce to make a single drop or split big drop split into ‘n’ number of drops, in both the cases energy is released/absorbed. Formula for is also stated herewith. In the next episode we discuss fluid dynamics where by liquid will start flowing.
